Exploring Model Inheritance in Django: A Guide for Efficient Code Reuse
Model inheritance is a powerful feature that allows developers to create modular and reusable code, significantly reducing redundancy and enhancing maintainability. This article delves into the three types of model inheritance in Django—multi-table inheritance, abstract base classes, and proxy models—providing practical examples to illustrate how each can be effectively utilized in your Django projects.
1. Multi-Table Inheritance: Structure with Connectivity
Multi-table inheritance is the go-to choice when you need to create a clear hierarchical structure between related models. In this approach, each model in the inheritance chain translates into a separate database table, linked through a OneToOne relationship.
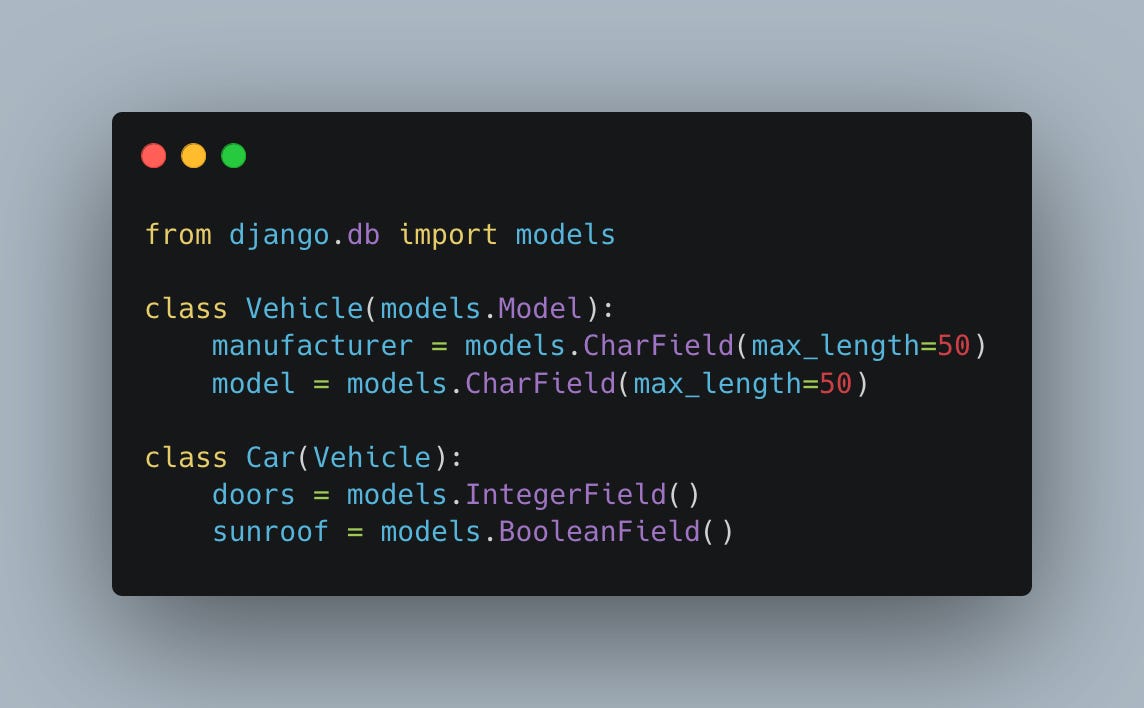
Consider an example where you're modeling vehicles:
Here, Car inherits from Vehicle, leading to two database tables. The Car table includes a OneToOne field to Vehicle, ensuring a direct linkage between the specific car and its general vehicle properties.
2. Abstract Base Classes: Template Models
When you aim to create a common template for other models without necessitating a corresponding database table for the base model, abstract base classes shine. This method is ideal for defining a common set of fields and methods to be shared across various child models.
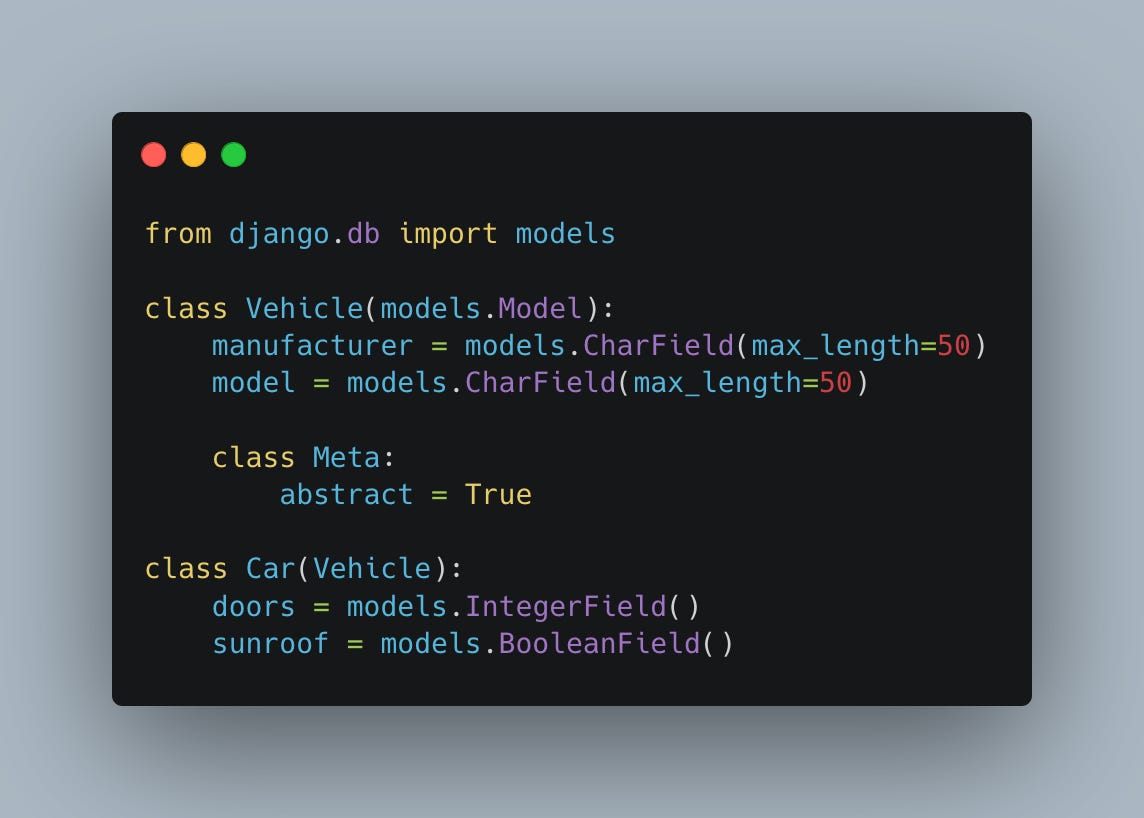
Here's how you can define a vehicle model as an abstract base:
Vehicle serves as a blueprint, and no separate table is created for it. Instead, Car will have its own table, incorporating both the attributes defined in Car and those inherited from Vehicle.
3. Proxy Models: Behavior Over Structure
Proxy models are your choice when you want to modify the behavior of a model but not its structure. Using this approach, the proxy model shares the same database table as its parent but can have different behaviors and methods.
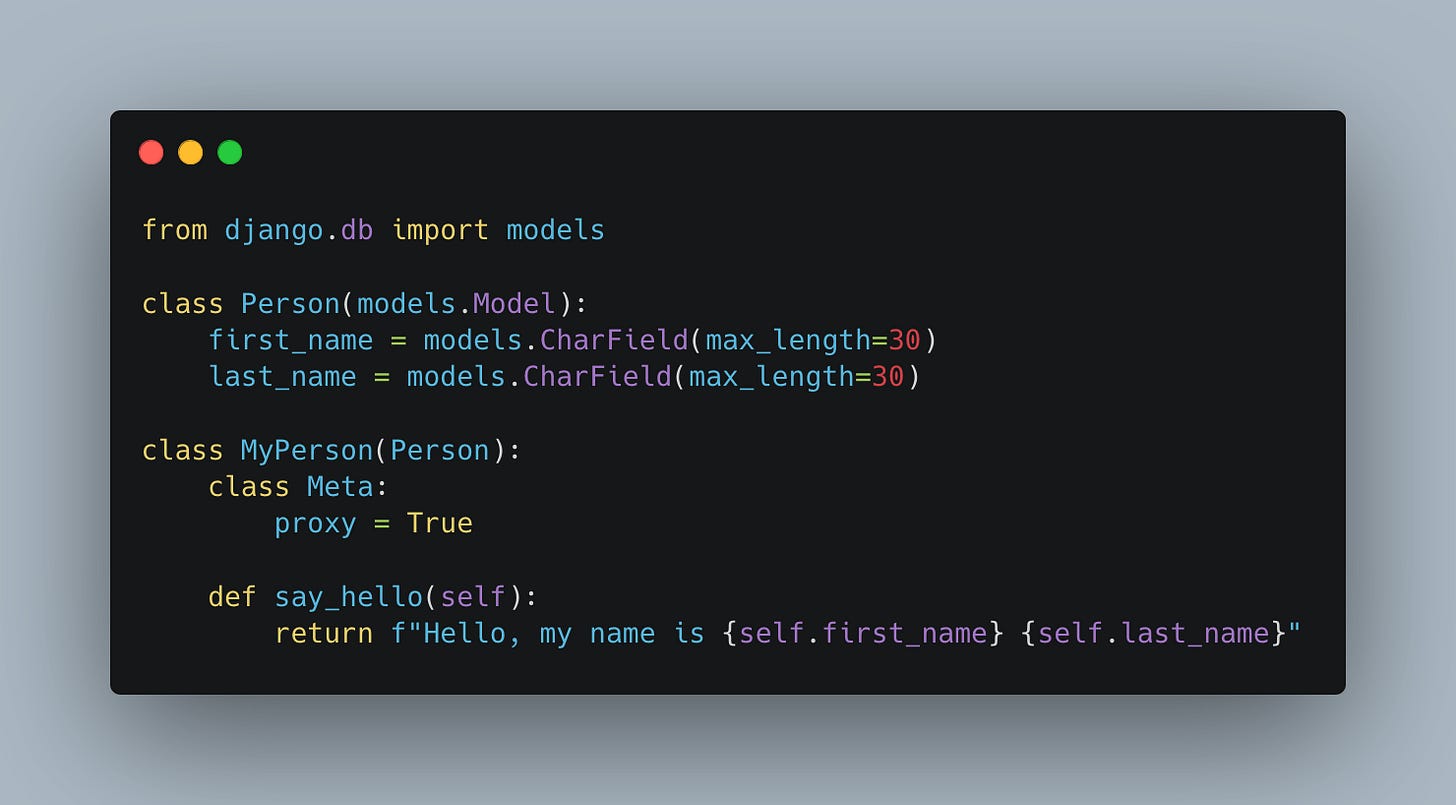
For instance, extending the functionality of a Person model:
MyPerson doesn't create a new table; it uses Person's table while introducing a new method or modifying existing behavior.
Making the Right Choice
Selecting the appropriate form of inheritance in Django depends on your specific requirements—whether you need separate tables, a shared template, or just a different set of behaviors. By leveraging these inheritance types, you can create more maintainable, scalable, and cleaner Django applications, making your development process more efficient and your codebase more robust.
✨ Bonus: Streamlining Your Django Development with Pre-commit Hooks
To further enhance your Django development workflow, incorporating tools like pre-commit can be a game-changer. Pre-commit is a framework for managing and maintaining multi-language pre-commit hooks. It streamlines the process of using git hooks to improve code quality, enforce coding standards, and identify simple issues before submission to code review.
What is Pre-commit?
Pre-commit allows you to configure various hooks that automatically check and format your code when you commit changes. This ensures that all commits meet your project's coding standards and helps in maintaining a clean and consistent codebase.
Setting Up Pre-commit for a Python/Django Project
Here's a simple guide on how to set up pre-commit for a Python/Django project to ensure your code is in tiptop shape before it even reaches a repository.
1. Install Pre-commit
First, you need to install the pre-commit package. It's recommended to install it as a global tool using pip:
pip install pre-commit2. Create a .pre-commit-config.yaml File
This file will contain the configuration for the hooks you want to use. Create this file in the root directory of your project. Here's a basic example that includes some common hooks for Python projects:
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v3.4.0 # Use the latest version
hooks:
- id: trailing-whitespace
- id: check-yaml
- id: end-of-file-fixer
- id: check-ast
- id: check-docstring-first
- repo: https://github.com/psf/black
rev: 22.1.0 # Use the latest version
hooks:
- id: black
language_version: python3
- repo: https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8
rev: 3.9.2 # Use the latest version
hooks:
- id: flake8This configuration includes:
Basic hooks from
pre-commit-hooksto fix trailing whitespace, check YAML files, ensure files end with a line break, validate syntax trees, and check that docstrings appear first in modules.The
blackformatter to automatically format your Python code.The
flake8linter to check for Python coding style and syntax errors.
3. Install the Git Hook Scripts
Run the following command to set up the git hooks:
pre-commit installThis command installs the pre-commit script in your .git/hooks/pre-commit directory.
4. Making a Commit
Now, when you make a commit, pre-commit will automatically run the configured hooks. If any changes are made or errors are found, the commit will be stopped, allowing you to make necessary adjustments.
Benefits of Pre-Commit
Incorporating pre-commit into your development workflow brings a host of benefits that can significantly enhance the quality and consistency of your codebase. Here are some of the key advantages of using pre-commit in your Django or any Python project:
Consistent Code Quality: Pre-commit ensures that every commit adheres to defined coding standards and best practices, promoting a consistently high code quality across the project. This consistency is crucial for maintaining readability and understandability, especially in collaborative environments.
Early Bug Detection: By running checks before code is even committed, pre-commit can catch potential issues early in the development cycle. This early detection helps in reducing the bug count in the later stages of development and can significantly streamline the debugging process.
Time-Saving: Catching and fixing issues before they make it to the repository can save time both for the individual developer and the team. It reduces the amount of time spent on code review and on fixing issues that could have been caught earlier.
Streamlined Development Process: Pre-commit automates the process of code validation, ensuring that developers don't have to remember to run checks manually. This automation helps in streamlining the development process, making commits smoother and more efficient.
Customizable and Extensible: Pre-commit supports a wide array of hooks for various languages and frameworks. You can tailor the tool to fit the specific needs of your project, choosing from a plethora of available hooks or even creating your own.
Improved Collaboration: When working in a team, ensuring that everyone adheres to the same coding standards can be challenging. Pre-commit enforces these standards automatically, ensuring that all contributions meet the project's requirements, which is particularly beneficial in collaborative projects.
Integration with Continuous Integration (CI) Systems: The checks performed by pre-commit can be aligned with those used in your CI/CD pipelines, ensuring consistency between local development and the CI/CD processes. This alignment can help in reducing the number of CI builds that fail due to code quality issues.
Enhanced Code Review Efficiency: With pre-commit handling the basic code quality and style checks, code reviewers can focus on more substantial aspects of code review, such as design patterns, architecture, and functionality. This focus can improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the code review process.